Power Delivery (PD) and Programmable Power Supply (PPS) are two critical protocols for USB-C charging. But how do they differ, and which is better for you?
PD provides fixed voltage levels for universal fast charging, while PPS adds flexible voltage control for faster, cooler, and more efficient charging.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the best charger for your device.
What is USB PD and how does it work?
USB Power Delivery (PD)[^1] is a universal fast-charging protocol supported by USB-C connectors. It delivers power at fixed voltage levels.
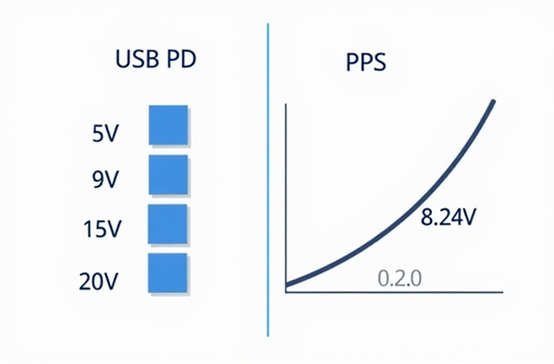
USB PD supports fixed voltages of 5V, 9V, 15V, and 20V, with a +/- 5% tolerance.

Dive-Deeper: Key Features and Benefits of USB PD
USB PD works across laptops, phones, and other devices. It provides high power but uses fixed Power Delivery Objects (PDOs).
USB PD Specifications:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Levels | Fixed at 5V, 9V, 15V, and 20V |
| Power Range | Capable of delivering up to 240W |
| Device Compatibility | Universal for most USB-C devices |
| Heat Management | Less efficient due to fixed voltage steps |
USB PD is widely adopted because of its reliability and high power output. However, its fixed voltage structure limits efficiency for modern devices requiring precise power delivery.
What is PPS and why is it important?
PPS(Programmable Power Supply)[^2] is an optional extension of USB PD 3.0 and USB PD 3.1. It allows dynamic control of voltage and current, enhancing charging efficiency.
PPS adjusts voltage in small steps of 0.02V, enabling faster and cooler charging.
Dive-Deeper: How PPS Enhances Power Delivery
Unlike PD, which works with fixed voltage levels, PPS adds Programmable Power Objects (PPOs). It allows the charger and device to negotiate the exact power needed.
Key Features of PPS:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Adjustment | Dynamic in 0.02V increments |
| Heat Generation | Reduced due to more precise power control |
| Device Optimization | Ideal for modern devices needing fine control |
| Power Efficiency | Higher efficiency due to outsourced conversion |
PPS chargers shift the power conversion process to the adapter rather than the device. This reduces heat generation, improves efficiency, and allows faster charging while keeping the device cooler.
How are PD and PPS related?
PPS builds on top of USB PD 3.0 and 3.1 specifications. A charger with PPS support is also USB PD compliant, but not all PD chargers support PPS.
PPS implies USB PD compatibility, but USB PD alone does not guarantee PPS support.

Dive-Deeper: Understanding PD vs. PPS Compatibility
USB PD relies on fixed Power Delivery Objects (PDOs), whereas PPS introduces Programmable Power Objects (PPOs).
| Feature | USB PD | PPS |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Levels | Fixed at 5V, 9V, 15V, and 20V | Adjustable in 0.02V steps |
| Dynamic Control | Not supported | Fully supported |
| Heat Management | Moderate | Improved, with lower heat generation |
| Device Compatibility | Universal | Limited to PPS-compatible devices |
Some USB PD chargers, even those with high power ratings, may not include PPS support. Manufacturers often limit PPS to specific wattages, like 18W, assuming it is only relevant for phone charging. Always check the charger’s specifications to confirm compatibility.
Why does PPS matter for modern devices?
Modern devices, especially flagship smartphones, benefit greatly from PPS[^3]. Brands like Samsung[^4] and ZTE have adopted PPS for their fast-charging systems.
PPS enables dynamic voltage adjustments, optimizing charging efficiency while reducing heat.

Dive-Deeper: Key Advantages of PPS for Modern Devices
PPS enhances charging performance by communicating directly with a device’s battery management system.
Benefits of PPS:
- Heat Reduction: PPS minimizes heat by fine-tuning voltage and current.
- Faster Charging: Dynamic voltage control enables higher speeds without extra heat.
- Battery Longevity: Lower heat prevents stress on the battery, extending its life.
Devices with PPS support can charge more efficiently, reducing energy loss and delivering a better user experience.
Should you choose PD or PPS chargers?
The choice depends on your device’s compatibility. USB PD chargers offer broad support, while PPS chargers provide superior performance for modern devices.

Dive-Deeper: PD vs. PPS Charger Checklist
| Feature | Choose PD | Choose PPS |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | For universal charging needs | For modern devices needing dynamic power |
| Charging Speed | Standard | Faster charging speeds |
| Device Heating | Higher due to fixed voltage levels | Lower with dynamic voltage control |
| Power Efficiency | Less efficient | More efficient, with reduced conversion loss |
For laptops or older devices, USB PD chargers are sufficient. If you own a PPS-compatible device, investing in a PPS charger ensures the best charging experience.
Conclusion
USB PD delivers universal fast charging, but PPS enhances it with dynamic voltage control, resulting in faster, cooler, and more efficient power delivery. Choose PPS for modern devices ,while PD is classic.
How to Confirm If Your Device Supports PPS
- Check the Manual: Look for charging protocols in the device's manual.
- Look for Labels: Some devices have PPS or Programmable Power Supply labels near the charging port.
- Visit Manufacturer’s Website: Find the device's tech specs on the manufacturer's website.
- Contact Support: Ask the manufacturer's support team if the device supports PPS.
Below is a table of mainstream brand products on the market that support PPS.
| Type | Brand | Model |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Samsung | Galaxy Note 10 series, Galaxy S20 series, Galaxy S21 series, Galaxy S23 Ultra, Galaxy A35 5G |
| OnePlus | 8T, 9, 9 Pro, 7 Pro, 7T, 7T Pro, Nord, N10, 8 Pro | |
| Xiaomi | Mi 9, Mi 10, Mi 11, Mi 12, Mi 12 Pro | |
| Huawei | P30, P40 Series, Mate 30 Series, Mate Xs, Nova 7 Series | |
| LG | V60 ThinQ, G8 ThinQ | |
| Pixel 4, Pixel 4 XL, Pixel 5, Pixel 6, Pixel 7 | ||
| Motorola | Moto G7, Moto G8, Moto G9, Moto X4, Edge | |
| Sony | Xperia 1, Xperia 5, Xperia 10 | |
| Oppo | Reno, Reno 2, Reno 3 | |
| Vivo | X21, X27, X50 | |
| Nokia | 8.3 5G, 9 PureView, 7.2 | |
| ZTE | Axon 10 Pro, Axon 11, Axon 20 | |
| Tablets | Apple | iPad Pro 11-inch (2nd gen+), iPad Pro 12.9-inch (3rd gen+), iPad Air (4th gen+), iPad Mini (5th gen+) |
| Laptops | Dell | XPS 15 9500, XPS 16, XPS 13 9300, Latitude 14 7420, Precision 5750 |
| HP | Spectre x360 14, Envy x360 13, Omen 15, EliteBook 840, EliteBook 850 | |
| Lenovo | Legion 5, ThinkPad X1 Carbon, Yoga 9i, ThinkPad T14, ThinkPad X1 Yoga | |
| ASUS | ROG Zephyrus G14, ZenBook 14, ROG Strix Scar 15, VivoBook 15 | |
| Accessories | Anker | SOLIX BP1600 Expansion Battery, 737 MagGo Charger (3-in-1 Station), MagGo Wireless Charging Station (15W, Foldable 3-in-1) |
As of 2024, newer models of many smartphones and laptops tend to support the PPS (Programmable Power Supply) charging protocol. This trend is driven by the industry's focus on optimizing charging efficiency and reducing heat generation to prolong battery life.
Power strips (HW-299PD, HW-300PD/SPD,HW-301PD)
support PPS for flexible and fast charging, protecting your devices.

References
-
USB Implementers Forum, Inc. (2020). USB Power Delivery. Retrieved from
https://www.usb.org/document-library/usb-power-delivery -
USB Implementers Forum, Inc. (2020). Universal Serial Bus Revision 3.1 Specification. Retrieved from
https://www.usb.org/document-library/usb-31-specification -
Kim, M. S., & Yun, K. S. (2016). Fast Charging Methods Using USB Power Delivery Technology. In IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics (Vol. 31, Issue 5, pp. 3514-3521). doi:10.1109/TPEL.2015.2489852
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7352400/ -
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (2018). Programmable Power Supply (PPS) for Fast Charging. Retrieved from
https://developer.samsung.com/tech-insights/fast-charging -
Piquemal, P. B., Gaddam, V. R., & Joubert, F. (2018). Advantages of Programmable Power Supply in Fast Charging Applications. In Journal of Power Sources (Vol. 396, pp. 701-710). doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.06.076
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.06.076







