Introduction
When we think about the electrical systems that power our homes, industries, and cities, circuit breakers might not be the first thing that comes to mind. However, these small but mighty devices play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of our electrical infrastructure.
A circuit breaker acts as an automatic switch that protects an electrical circuit from damage due to overcurrent or short circuits. It prevents electrical fires, protects appliances, and ensures the overall safety of an electrical system. In this blog post, we'll explore circuit breakers from various perspectives, their working principles, and the different types available today.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
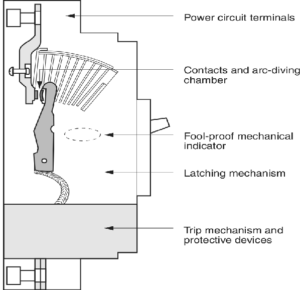
A circuit breaker is a safety device designed to interrupt the flow of electricity when an overload or fault is detected. Unlike fuses, which must be replaced after blowing, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping, making them reusable and cost-effective.
Key Functions of a Circuit Breaker:
- Overload Protection: Prevents excessive current from damaging electrical wiring.
- Short Circuit Protection: Stops the flow of electricity if a fault occurs.
- Fire Prevention: Reduces the risk of electrical fires by cutting power when needed.
- System Reliability: Ensures smooth operation of electrical networks by isolating faults.
The Importance of Circuit Breakers
Electrical Engineering Perspective
From an electrical engineering standpoint, circuit breakers are vital for maintaining stable and safe electrical networks. They act as a first line of defense against system failures, ensuring that electrical installations operate efficiently without overheating or overloading.
Safety Perspective
Circuit breakers are a critical component in fire prevention and electrical safety. By automatically disconnecting power when a fault is detected, they reduce the risk of electrocution, electrical fires, and damage to appliances and wiring.
Homeowner Perspective
For homeowners, circuit breakers provide peace of mind. If a breaker trips, it often signals an issue such as an overloaded circuit, faulty wiring, or a malfunctioning appliance. By identifying these issues early, homeowners can take corrective action before a more serious electrical hazard develops.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, circuit breakers protect expensive machinery and equipment from electrical faults. Factories, data centers, and commercial buildings rely on circuit breakers to prevent costly downtime and maintain operational efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Modern circuit breakers are designed with sustainability in mind. Many feature energy-efficient designs, longer lifespans, and eco-friendly materials. As the electrical industry moves towards greener solutions, circuit breakers continue to evolve to reduce waste and improve energy efficiency.
How Do Circuit Breakers Work?
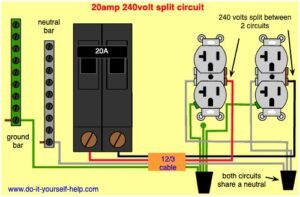
Circuit breakers operate through a simple yet highly effective mechanism:
- Detection: Built-in sensors detect abnormal conditions such as excessive current or a short circuit.
- Interruption: The breaker quickly opens its internal contacts, stopping the flow of electricity to prevent damage.
- Resetting: After the fault is cleared, the breaker can be manually or automatically reset to restore power.
By quickly responding to electrical faults, circuit breakers minimize hazards and ensure the continuous operation of electrical systems.
Types of Circuit Breakers
There are several types of circuit breakers, each designed for specific applications and safety requirements:
1. Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
- Used in residential and commercial buildings.
- Compact size, typically rated up to 100 amps.
- Protects against overloads and short circuits in smaller electrical systems.
2. Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs)
- Designed for industrial and commercial applications.
- Higher current ratings (up to 2,500 amps) and adjustable trip settings.
- Suitable for protecting large electrical circuits and heavy-duty machinery.
3. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
- Protect against ground faults and electrical shocks.
- Commonly used in bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas where moisture is present.
- Automatically disconnects power if an imbalance in current flow is detected.
4. Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs)
- Protect against arc faults, which can cause electrical fires.
- Required in many modern homes, particularly in bedrooms and living rooms.
- Detects dangerous electrical arcs and cuts power to prevent fire hazards.
5. High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
- Used in power transmission and distribution networks.
- Designed for voltages above 1,000 volts, with remote operation capabilities.
- Essential for maintaining stability in large-scale electrical grids.
6. Vacuum Circuit Breakers
- Commonly used in industrial and utility applications.
- Uses vacuum as the arc-extinguishing medium, suitable for voltages up to 38 kV.
- Offers long service life and minimal maintenance.
7. Oil Circuit Breakers
- Used in high-voltage power transmission systems.
- Uses oil as an insulating and arc-quenching medium.
- Effective for extremely high voltage applications but requires periodic maintenance.
8. Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs)
- Used in low and medium voltage applications.
- Uses air as the arc-extinguishing medium.
- Typically rated for currents up to 6,300 amps and found in industrial switchboards.
Circuit Breakers in Power Strips: An Essential Safety Feature
Power strips are a common household and office accessory, allowing multiple devices to connect to a single power source. However, without proper protection, they can become a fire hazard due to overloads or short circuits. This is where circuit breakers play a crucial role in ensuring safety.
How Circuit Breakers Enhance Power Strip Safety
A power strip with a built-in circuit breaker provides an extra layer of protection against electrical hazards. Here’s how it works:
- Overload Protection: If the total power demand exceeds the strip’s rated capacity, the circuit breaker trips, cutting off power to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Short Circuit Protection: If a sudden surge or fault occurs, the breaker immediately interrupts the flow of electricity, reducing the risk of sparks and damage to connected devices.
- Resettable Design: Unlike fuses that need to be replaced after blowing, power strip circuit breakers can be reset, making them more convenient and cost-effective.
Why Quality Matters in Power Strip Circuit Breakers

Not all power strips offer the same level of protection. High-quality power strips incorporate:
- Thermal and Magnetic Circuit Breakers: These offer dual protection against both prolonged overloads and sudden spikes.
- Optimized Spacing Between Outlets: Reducing overheating risks by allowing better airflow and minimizing plug interference.
- High-Quality Internal Components: Using premium wiring and durable casings to improve safety and longevity.
At Aligator Power, we've continuously improved our power strip designs over the years. Initially, we followed the standard outlet spacing of 28mm, but we later expanded it to 39mm to enhance safety and prevent overheating caused by closely packed plugs. This small yet significant design change, combined with robust circuit breaker protection, ensures that our power strips offer both convenience and superior safety.
Choosing the Right Power Strip with a Circuit Breaker
When selecting a power strip, consider the following:
| Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Circuit Breaker Type | Thermal or magnetic breakers provide better protection. |
| Surge Protection | Additional safety against voltage spikes and lightning. |
| Outlet Spacing | Wider spacing prevents overheating and physical obstructions. |
| Certification | Look for UL, ETL, or CE-certified power strips for guaranteed safety. |
By investing in a power strip with a built-in circuit breaker, you’re not only protecting your electronic devices but also safeguarding your home or workplace from potential electrical hazards.
Next time you purchase a power strip, check for a circuit breaker—it could be the small feature that prevents a major accident.
Conclusion
Circuit breakers may not always be in the spotlight, but their importance in ensuring electrical safety and reliability cannot be overstated. Whether in homes, industries, or power networks, these devices protect us from electrical faults and ensure the smooth functioning of our electrical systems.
As technology advances, circuit breakers continue to evolve, offering better protection, greater efficiency, and more sustainable designs. By understanding their role, we can appreciate how these unsung heroes work tirelessly behind the scenes to keep our homes and workplaces safe.
Next time you flip a switch, take a moment to acknowledge the circuit breaker—your silent guardian against electrical hazards.








